DIFFERENCE BETWEEN POSITIVE/NEGATIVE REINFORCEMENT AND POSITIVE/NEGATIVE PUNISHMENT
As kids grow up, they learn about acceptable and non-acceptable behaviors through the response they get from their environment.
According to the way kids behave, we give feedback to kids to act in a certain way so that they either repeat more of the good behaviors or stop repeating misbehaviors.
Psychologists have classified the way we give feedback to kids as reinforcement and punishment.
According to psychology.iowa.edu,
Reinforcement is defined as a consequence that follows an operant response that increase (or attempts to increase) the likelihood of that response occurring in the future.
And punishment is defined as,
The infliction or imposition of a penalty as retribution for an offence.
SO, WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN REINFORCEMENT AND PUNISHMENT?
Reinforcement is used when you want your kids to repeat certain behaviors in the future.
Punishment is used when you want your child to stop doing a certain act or behavior.
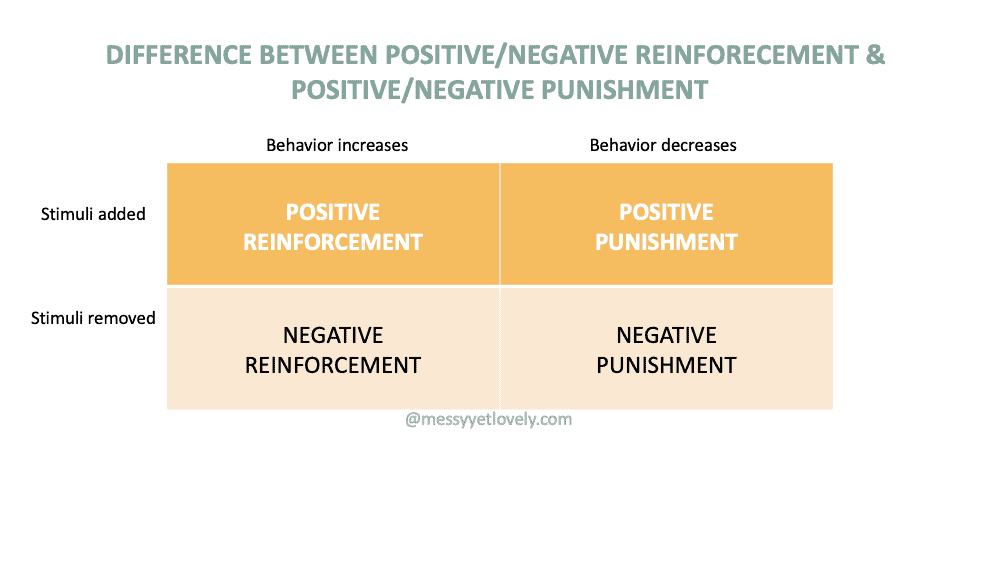
Both punishment and reinforcement can be positive or negative.
Let’s dive deep into each category.
TYPES OF REINFORCEMENT
Reinforcement can be divided into two types: positive reinforcement and negative reinforcement.
WHAT IS POSITIVE REINFORCEMENT?
Positive reinforcement is, giving out a positive response after a behavior that makes the likelihood of the same event happening again in the future.
When a positive reward, praise, or feedback follows after an event, the behavior gets strengthened. And the doer feels the urge to repeat it again in the future.
For example, if a child prepares well and earns a prize for a quiz program, the child becomes happy and is proud of the effort he took to prepare.
This will motivate him to do it again and again. And this can spill onto other areas as well because he learns that if he prepares and practices well, he can gain rewards again in the future.
Here, the positive reinforcement happened naturally.
But parents can reinforce positive behavior in different ways so that kids learn to do more of the good behaviors.
It’s always good to give attention to positive behaviors more so that such behaviors increase naturally.

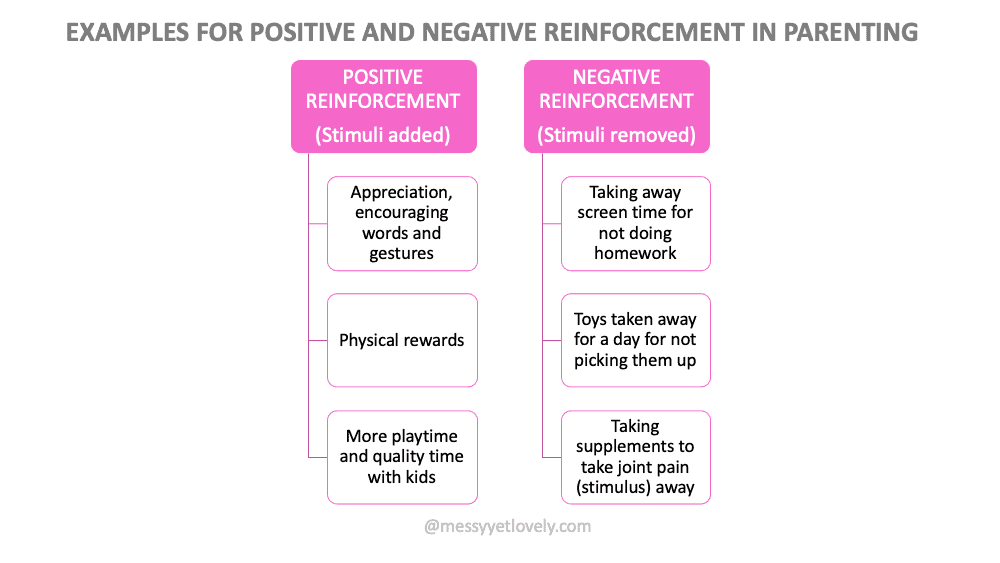
EXAMPLES OF POSITIVE REINFORCEMENT
Positive reinforcement can be done using words, gestures, or tangible rewards -whichever is appropriate for the situation.
Examples are:
- Encourage their effort using words like, “I appreciate you working hard for the exam. You must be proud of yourself”. Make sure you encourage their effort more than the final result.
- Gestures like patting on their back, rubbing softly on their head, giving a handshake, or a high-five.
- Physical rewards (it should not be always encouraged but can be done occasionally with big milestones)
- Extra privileges like more playtime for finishing their work sooner or more quality time with them
Related: 30 family rituals to start to bring your family closer
Please remember that kids are not always diligent to finish their chores or responsibilities and they get distracted easily.
Even so, instead of focusing on what they did not get done, focus and encourage them for showing initiative and taking action.

WHAT IS NEGATIVE REINFORCEMENT?
Though negative reinforcement can sound “negative”, it is not negative.
Here, the word “negative” implies “taking away” or “removing something present” or “avoiding an aversive stimulus resulting from the behavior”.
It is a bit tricky to understand negative reinforcement, as we can easily confuse it with punishment.
Negative reinforcement means you are taking something away to strengthen a behavior.
For example,
- If your child doesn’t finish the homework on time, you reduce their screen time or do not give devices at all.
Here the aversive stimulus is – removal of screen time.
And the behavior you want to strengthen is – finishing homework on time.
Example 2:
- A child not picking up toys after playing loses the toys for a day.
Here the aversive stimulus is – losing the toys.
And the behavior you want to strengthen is – picking up the toys after playing.
Example 3:
- A child who refuses to take supplements experiences joint pain.
Here the aversive stimulus is – joint pain.
And the behavior that gets strengthened is – taking supplements.
Once a child learns from his experience, he probably wouldn’t forget to take his supplement next time because he wants to avoid the aversive stimulus, which is, getting joint pain.
Therefore the behavior is strengthened.
Hence, negative reinforcement is not a bad thing. And sometimes we need to use both types of reinforcement according to the situation.
Reinforcement, be it positive or negative, should be put into practice immediately after the behavior for it to be effective.
POSITIVE REINFORCEMENT VS NEGATIVE REINFORCEMENT
To sum it up, reinforcement is used to encourage a behavior.
When using positive reinforcement we add something to the situation. And when using negative reinforcement, we remove something from the situation.
Negative reinforcement is usually made to remove unpleasant outcomes while positive reinforcement is done to receive something.
That being said, parents can fall into the accidental trap of negative reinforcement.
Many parents usually set rules and boundaries.
But sometimes they give in to the whining or tantrums of kids. This sends the message to kids that when they whine, the rules can be broken.
So for kids, the aversive stimuli (rules) can be taken away with behavior (whining).
And for parents, aversive stimuli (whining) can be taken away with behavior (giving in).
This cycle is not easy to break unless the parent decides to stay firm.

WHAT IS POSITIVE PUNISHMENT?
As said earlier, punishment is used to discourage a behavior from repeating.
Just like we talked about reinforcement, here positive or negative doesn’t mean good or bad.
Positive means adding a consequence and negative means removing a consequence.
Positive punishment means adding an aversive consequence after an unwanted behavior is exhibited.
Positive punishment need not always be introduced by caregivers or authority figures. Sometimes there are natural consequences to unwanted behaviors, and that can act as positive punishment too.
For example,
- Getting wet after forgetting to take an umbrella
- Failing in exam after not studying
- A child touching an electric socket and getting a shock
Through natural consequences, one learns why they should not do a certain action and the behavior is naturally decreased to avoid the consequence.
And consequences are an important part of positive parenting because children learn the effect of their actions through consequences.
But sometimes, the consequence or aversive stimuli are introduced by others.

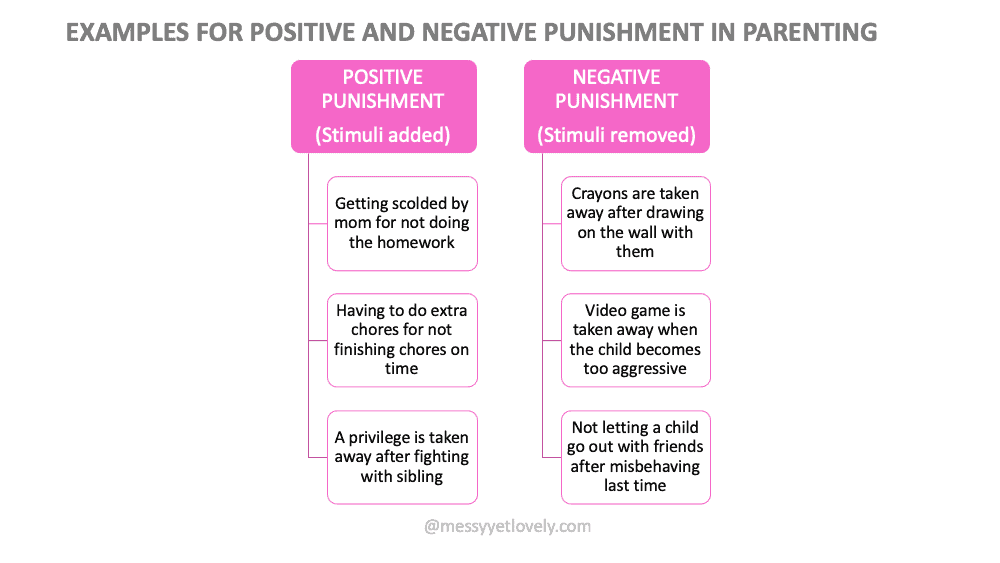
Examples of such positive punishment:
- Getting scolded by teacher for not listening in the class
- Having to do extra chores for not finishing chores on time
- A privilege is taken away after fighting with a sibling
Even though natural consequences can be effective in teaching the desired behavior, positive punishment may not always be effective in teaching kids the desired behavior.
Usually, when parents punish children, they try to be good at their behaviour only because they want to avoid punishment.
But they still may not develop the intrinsic desire to be at their best behavior when the authority figures are not around.
Hence, reinforcement is always better at encouraging good behaviour and developing intrinsic motivation.
Through reinforcement, there is more probability of kids trying to increase positive behaviour.
WHAT IS NEGATIVE PUNISHMENT?
Negative punishment is taking away a pleasant stimulus in order to discourage a behavior.
Examples of negative punishment for kids:
- A child draws with crayons on the walls and parents take away the crayons
- A child becomes aggressive after continuously playing video games and therefore the video game is taken away
- Not letting the child go for outing with friends because he misbehaved last time.
How does punishment differ from negative reinforcement and how does punishment affect behavior?
Reinforcement is implemented to strengthen a behavior whereas punishment is given to reduce it.
But punishment usually doesn’t eliminate the behaviour, it only suppresses it.
Sometimes it might teach kids the lesson you intended, but at the same time, a fear gets induced in his mind about you which is undesirable.
Psychologists agree that reinforcement is better than punishment because it strengthens good behaviour.
For example,
If you punish your kids for fighting with each other, they may act well in front of you and repeat the behaviour when you are not around.
But instead of that, whenever you catch them behaving well with each other, you encourage the kindness and love between them and the unity between them are strengthened too.
Negative reinforcement is not a form of punishment as reinforcement is intended to strengthen behavior and punishment is used to decrease a behavior.
In negative reinforcement, something unpleasant is removed to strengthen a behavior while in positive punishment something unpleasant is added to weaken a behaviour.
Since an unpleasant stimulus is removed in negative reinforcement, it cannot be considered a punishment.
For example:
Removing grounding rules when a teenager starts acting responsibly.
In short, here is a useful representation of all that you learned about in a nutshell.
 FINAL THOUGHTS
FINAL THOUGHTS
There is no right or wrong when it comes to deciding which consequence or punishment to implement. And it depends on what the situation demands and what works for your family.
But in general, positive reinforcement is better when you want to make a habit more consistent.
And negative reinforcement is better when you want to change a negative behaviour when it is well-established. In the case of negative reinforcement, we are enforcing positive behavior by taking away something.
